By Desmond Nleya
Hookworm disease is a parasitic infection caused by small intestinal worms that feed on the host’s blood, leading to significant health issues if left untreated. It is a major public health concern in tropical and subtropical regions, particularly in communities with poor sanitation. Understanding this disease is essential for effective prevention and control.
What Is Hookworm Disease?
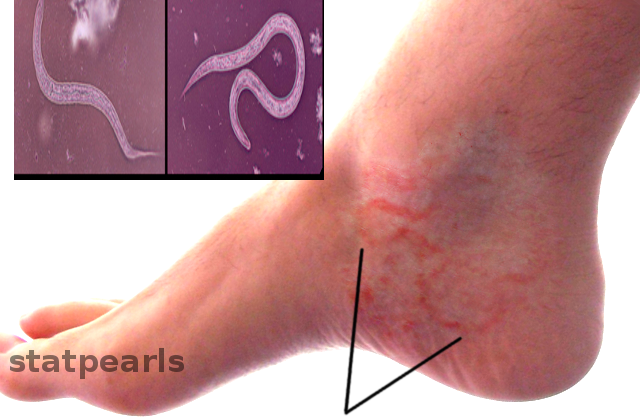
Hookworm disease occurs when hookworm larvae penetrate the human skin or are ingested, eventually reaching the small intestine where they attach and feed on blood. The two main species infecting humans are Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus.
The infection is part of a group of neglected tropical diseases and is common in areas with warm, moist climates where sanitation is inadequate.
Causes and Transmission
Hookworm infection is caused by exposure to hookworm larvae, which develop in soil contaminated with human feces containing hookworm eggs. The main transmission routes are:
Skin Penetration – Walking barefoot on contaminated soil allows larvae to burrow into the skin, usually through the feet.
Oral Ingestion – Consuming contaminated food or water can lead to infection.
Poor Sanitation – Open defecation and lack of proper waste disposal promote the spread of larvae.
Occupational Exposure – Farmers, miners, and construction workers in endemic areas are at higher risk.
Symptoms
The symptoms of hookworm disease depend on the severity of the infection and the parasite load. Common signs include:
Skin Irritation – Itchy rash at the site of larval entry (“ground itch”).
Respiratory Symptoms – Cough and wheezing as larvae migrate through the lungs.
Gastrointestinal Issues – Abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, and bloating.
Anemia – Fatigue, weakness, and pallor due to chronic blood loss.
Nutritional Deficiencies – Especially in children, leading to growth delays and cognitive impairment.
Severe, untreated infections may cause severe anemia and protein loss, posing life-threatening risks.
Prevention
Preventing hookworm disease focuses on breaking the cycle of transmission:
Proper Sanitation – Use of toilets and safe waste disposal to prevent soil contamination.
Wearing Footwear – Protects the skin from direct contact with contaminated soil.
Safe Water and Food Hygiene – Washing fruits and vegetables, boiling drinking water.
Health Education – Informing communities about hygiene and risks.
Mass Deworming Programs – Regular anti-parasitic medication distribution in high-risk areas.
Treatment and Cure
Hookworm disease is treatable with safe and effective medications. Commonly used drugs include:
Albendazole or Mebendazole – Single-dose oral anti-parasitics that kill the worms.
Iron Supplements – To treat anemia caused by blood loss.
Nutritional Support – To restore lost nutrients and promote recovery.
Early diagnosis and treatment prevent complications and help maintain community health.
Hookworm disease is preventable, treatable, and curable, yet it remains a burden in many developing regions due to poor sanitation and lack of awareness. Through improved hygiene, mass deworming, and public health education, the cycle of infection can be broken, saving lives and improving quality of life, especially among vulnerable populations.