By Staff Reporter
Understanding Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting men, particularly those over the age of 50. It develops in the prostate gland, a small walnut-shaped organ located below the bladder and in front of the rectum, responsible for producing seminal fluid. While the exact cause of prostate cancer is not always clear, it typically begins when cells in the prostate mutate and grow uncontrollably, forming a tumor that can potentially spread to other parts of the body.
Symptoms of Prostate Cancer
In its early stages, prostate cancer often has no noticeable symptoms. As the disease progresses, men may experience:
Urinary Problems – Increased frequency of urination, difficulty starting or stopping urination, weak urine stream, or painful urination.
Blood in Urine or Semen – Known as hematuria or hematospermia, which may indicate an advanced stage.
Erectile Dysfunction – Difficulty in achieving or maintaining an erection.
Pelvic Discomfort or Pain – Persistent pain in the lower back, hips, or thighs.
Unexplained Weight Loss and Fatigue – When cancer has advanced or spread beyond the prostate.
It is important to note that some of these symptoms may also be caused by non-cancerous conditions, such as prostate enlargement (benign prostatic hyperplasia). Therefore, medical evaluation is critical.
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the risk of developing prostate cancer:
Age – Risk increases significantly after age 50.
Family History – A father or brother with prostate cancer increases risk.
Race – African men are at a higher risk.
Lifestyle Factors – Poor diet, obesity, and smoking may contribute.
Prevention of Prostate Cancer
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent prostate cancer, certain lifestyle choices can help lower the risk:
Healthy Diet – A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and low in red or processed meats, may reduce risk.
Exercise Regularly – Physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and improves overall immune function.
Maintain a Healthy Weight – Obesity is linked to a more aggressive form of prostate cancer.
Regular Medical Checkups – Men over 50 (or over 40 with high risk) should consider prostate-specific antigen (PSA) testing and digital rectal examination (DRE).
Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol – These habits can contribute to overall poor health and higher cancer risk.
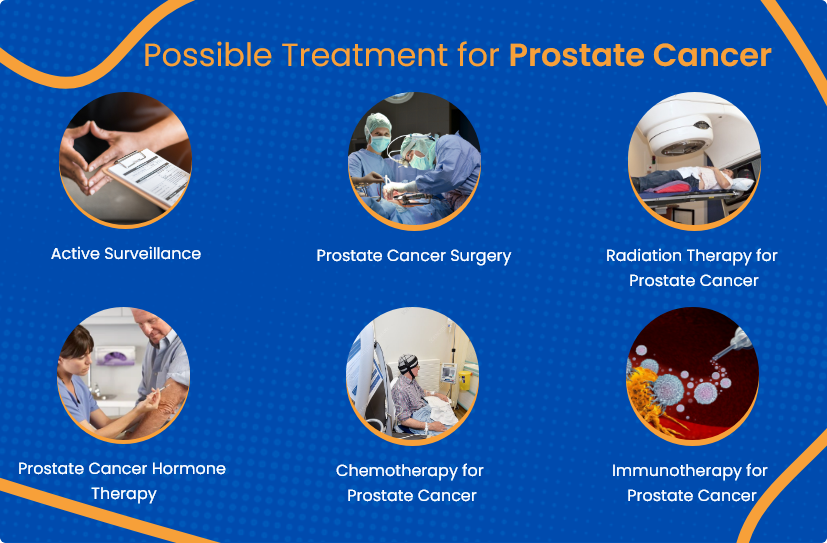
Treatment and Cure
The treatment of prostate cancer depends on the stage and aggressiveness of the disease as well as the patient’s overall health. Common treatment options include:
1. Active Surveillance
For slow-growing cancers that do not cause symptoms, doctors may monitor the cancer closely with regular PSA tests and biopsies, delaying aggressive treatment until necessary.
2. Surgery (Prostatectomy)
This involves the removal of the prostate gland and is often recommended for cancer that is confined to the prostate.
3. Radiation Therapy
High