By Desmond Nleya
Chickenpox, medically known as varicella, is a highly contagious viral infection that primarily affects children, though adults can contract it as well. It is caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV), a member of the herpesvirus family. Although often considered a mild childhood illness, chickenpox can lead to serious complications, especially in adults, pregnant women, and individuals with weakened immune systems.
Causes and Transmission
Chickenpox spreads easily from person to person through:
Direct contact with the fluid from the blisters
Respiratory droplets from coughing or sneezing
Touching contaminated surfaces or objects
An infected person becomes contagious 1-2 days before the rash appears and remains so until all the blisters have formed scabs — usually about 5 to 7 days after the rash begins.
Symptoms of Chickenpox
The symptoms typically appear 10 to 21 days after exposure to the virus. Early signs may resemble those of the flu or a cold, including:
Fever
Fatigue and general discomfort
Loss of appetite
Headache
These are followed by the hallmark symptom:
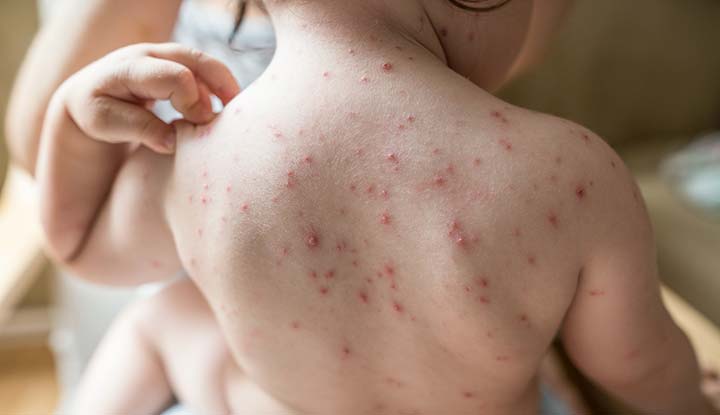
1. Skin Rash
Starts as red spots, often on the face, chest, and back, then spreads to other areas
Progresses to itchy fluid-filled blisters that eventually burst and crust over
Appears in crops over several days, meaning a person can have all stages of the rash at the same time
Other symptoms may include sore throat, irritability (especially in children), and muscle aches.
Complications
While most cases resolve without issue, complications can include:
Bacterial infections of the skin
Pneumonia
Encephalitis (inflammation of the brain)
Reye’s syndrome (especially in children given aspirin)
Birth defects if a pregnant woman is infected early in pregnancy
Shingles later in life, as the virus remains dormant in the body
Prevention of Chickenpox
The most effective way to prevent chickenpox is through vaccination.
1. Varicella Vaccine
Given in two doses
First dose: between 12 and 15 months
Second dose: between 4 and 6 years
Over 90% effective in preventing the disease
In addition:
Avoiding contact with infected individuals
Good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing
Isolation of infected individuals until blisters scab over
Treatment and Management
For healthy children, chickenpox is usually mild and treated at home.
1. Home Care
Rest and hydration
Paracetamol (acetaminophen) to reduce fever and pain (never give aspirin to children)
Calamine lotion or colloidal oatmeal baths to relieve itching
Trimmed fingernails to prevent skin infections from scratching
2. Antiviral Medications
Acyclovir or other antivirals may be prescribed for:
People at risk of severe disease (e.g., immunocompromised individuals)
Adults with early symptoms
Pregnant women or newborns exposed to the virus
3. Hospitalization
Severe cases may require hospital care, particularly if complications develop.
Conclusion
Chickenpox is generally a mild but uncomfortable illness that is preventable through vaccination. While most cases resolve without serious problems, awareness of potential complications and early care is crucial — especially in vulnerable populations. With proper vaccination, hygiene, and timely treatment, chickenpox can be effectively controlled and its impact minimized.
Key Takeaway:
Vaccinate. Isolate. Treat the symptoms. Seek help if complications arise.